Next Step, along with our partners and allies in affordable housing, recognizes the power of factory-built housing. It has the potential to play a pivotal role in addressing the housing supply and affordability crisis. However, it’s important to understand that not all factory-built housing is the same, and the differences can be subtle yet significant.
To effectively serve their clients and communities, affordable housing developers, zoning officials, housing counselors, and mortgage lenders should familiarize themselves with the various types of factory-built homes. Doing so ensures that the appropriate home type is selected for each unique homebuyer and situation. The following outlines the four categories of factory-built homes, highlighting their pros and cons, as well as their similarities and differences.
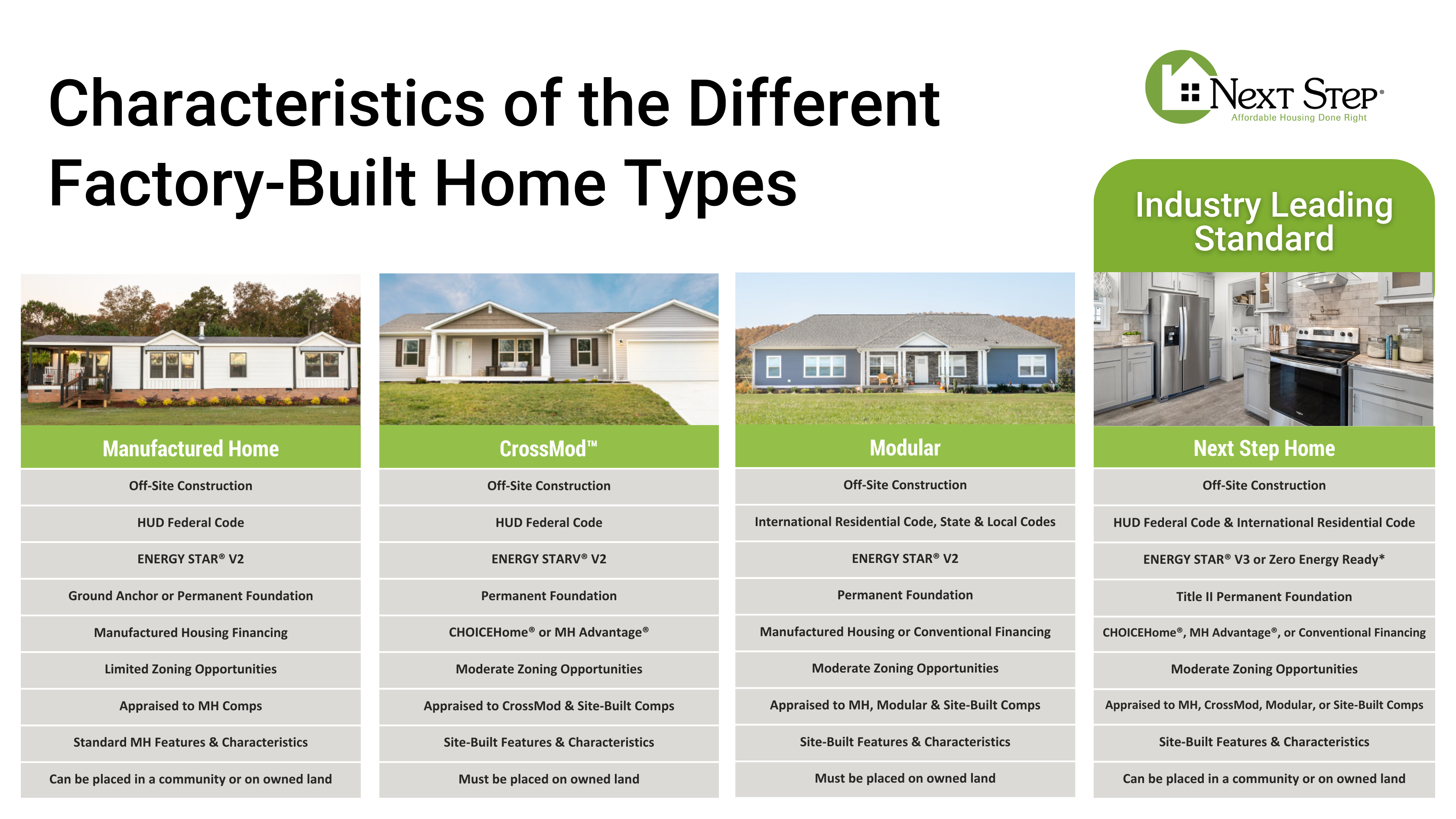
Comparing the Home Types
Key Similarities
All factory-built homes share certain advantages:
- Controlled Construction Environment: Built off-site, these homes are protected from weather delays and equipment theft, ensuring a higher level of quality control.
- Foundation Flexibility: Homes can be placed on permanent foundations, making them eligible for a range of financing options, including FHA, Freddie Mac, and Fannie Mae loans.
Key Differences
The main differences between factory-built home types lie in their design features and the building codes they must adhere to. Depending on the type of home, it may need to comply with the state and local building codes of the home’s location or the federal HUD code. Some home types are nearly indistinguishable from site-built homes, offering highly sought-after features such as garages and solar-ready construction.
Factory-Built Housing Category Breakdown
Next Step Homes
The Next Step Home is the leading standard for factory-built homes, offering enhanced energy efficiency, advanced foundation systems, and more.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Next Step Homes are ENERGY STAR® V3-certified or Zero Energy Ready, which can save homeowners 30-50% on monthly utility bills.
- Advanced Foundation Systems: Built to the Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards (HUD Code) on Title II Permanent Foundations.
- Versatile Financing Options: Qualify for FHA, USDA, VA, Freddie Mac’s CHOICEHome®, and Fannie Mae’s MH Advantage®.
- Flexible Placement: They can be placed on owned land or within existing manufactured housing communities.
CrossMod™ Homes
CrossMod homes blend modern design with factory-built efficiency:
- Design Features: Site-built elements such as garages and pitched roofs.
- Standards Compliance: Built to the HUD code and ENERGY STAR® V2 standards.
- Financing: Eligible for Freddie Mac’s CHOICEHome® and Fannie Mae’s MH Advantage® programs.
- Placement: Must be placed on land owned by the homebuyer.
Modular Homes
Modular homes have evolved significantly since their inception in 1958:
- Construction Standards: Built off-site to adhere to all applicable state and local codes of the home’s location.
- Flexibility: Can be purchased and placed on owned land using conventional mortgages or manufactured housing financing options.
- Design Variability: Building standards can vary by location, offering more customization compared to other factory-built homes.
Manufactured Homes
Manufactured homes represent the foundational model for factory-built housing:
- Affordability: The most cost-effective option with fewer site-built features.
- Placement Options: Installed on ground anchors or permanent foundations in manufactured housing communities or on owned land.
- Zoning and Financing: Limited by zoning restrictions with fewer financing options.
Understanding the distinctions between the factory-built home types is essential for making well-informed decisions in the affordable housing space. Each type offers advantages and considerations that can be leveraged in a variety of housing scenarios. Factory-built housing can help us all better navigate the complexities of affordable housing and provide solutions that prioritize homebuyers and communities.
Manufactured homes provide a cost-effective option with flexible placement options, although they may be limited by exclusionary zoning. CrossMod™ homes bridge the gap between manufactured and site-built homes, offering enhanced features and better zoning opportunities but requiring placement on owned land. Modular homes can be built to adhere to a range of building codes with similar zoning considerations to CrossMod™ homes. Next Step Homes excel in energy efficiency and provide versatile placement and financing options, making them the leading standard in factory-built homes.
By carefully evaluating the features, benefits, and placement requirements of each type of factory-built home, those in affordable housing can promote and provide sustainable and affordable housing solutions. Learn more about housing and community development with factory-built homes here.
Ready to integrate factory-built into your community’s affordable housing plan? Learn about our consulting services or contact us about your project here.